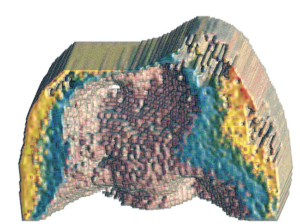
A novel method of creating 3D thermophotonic images developed by Andreas Mandelis (MIE) and his research team is highlighted in
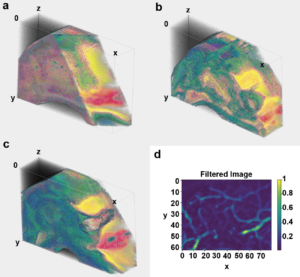
Photonics Media. Their method, called “truncated-correlation photothermal coherence tomography (TC-PCT)”, uses infrared camera frames to reconstruct 3D thermal images. This allows for sharp, depth-wise thermal images to be created in materials like living tissues that typically scatter light profusely. These materials normally give rise to diffuse optical and thermal images, but TC-PCT allows for thermal-wave localization which is necessary for the 3D thermal reconstruction revealing previously impenetrable optical absorption images.
This unique technology will have a great impact in biomedicine as it allows for detailed, non-invasive imaging to be completed, leading to early and more precise diagnoses and more successful treatments. This technology can be used to detect dental caries, early cancer growths and even to map blood vessels that may alert to cancer-triggered angiogenesis.